In VRML the selection of a LOD is performed by comparing ranges. A viewer switches to the next LOD if the distance of the LOD to the viewpoint is greater or equal to a specified value.
Switching from a LOD to the next means that representatives are selected
from clusters of points. All points within a cluster are moved to the representative.
The program calculates the range of a LOD so that the maximum deferral
of these points projected to the screen is below a specified value. This
value can be set with the commandline option -e
or --errorrange. If you
specifiy an errorrange of 10 this means the maximum deferral of the points
on screen is below 10% of the height of the screen. If you do not specify
this option a default value of 2% will be used.

How will this range be calculated ?
The viewer must switch to the next LOD if the maximum deferral s projected into the screen is greater than errorrange % of the height of the screen. The deferral s is defined by the diagonal of the smallest cube in the octree of the next LOD.
So s is calculated as follows:
s = scalefactor * sqrt(3) * (size of cube of root node) /
2depth of octree of next LOD -1
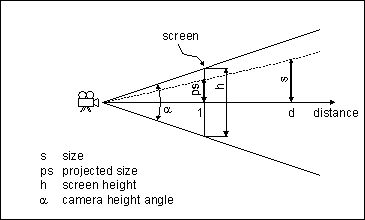
The points will be projected into a projection plane (the screen) with distance 1 to the camera. The height of the screen is determined by the camera height angle:
h = 2 * tan(alpha/2) * 1
The maximum deferral s projected into the screen is called ps. A viewer must switch to the next LOD if ps is greater than:
ps = errorrange/100 * h
Now the distance for switching can be calculated:
d/s = 1/ps => d = s/ps
Finally the formula for the distance d is:
d = s / (errorrange/100 * 2 * tan(alpha/2) )
The program adds to this distance d the radius of the bounding sphere of the coordinates in the next LOD.